Dna Polymerase Reads the Original Template Strand From the
The nucleotide base sequence of the template strand 3-5 is complementary to the base sequence of both the sense strand and the mRNA transcript 5-3. Either molecule moves down the strand in the 3 to 5 direction and at each subsequent base it adds the complement of the current DNA base to the growing nucleic acid.

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii
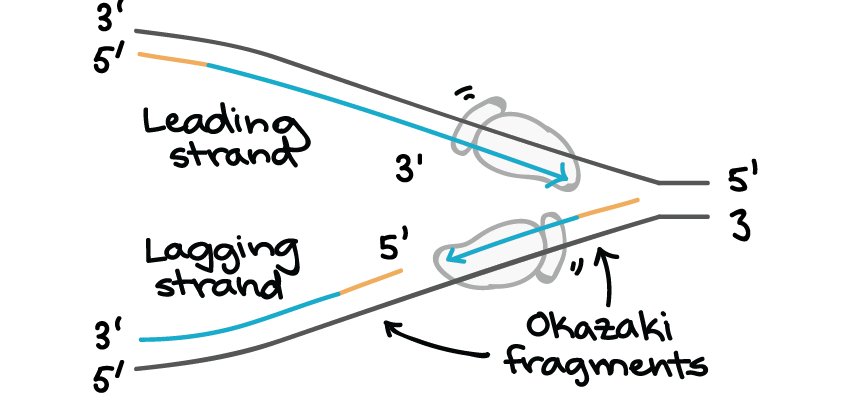
The lagging strand is the new strand that grows directly.

. DNA polymerases rapid catalysis is due to its processive nature. A specific template-checking function in a DNA polymerase has not been observed previously and it may represent the first. First RNA polymerase binds to an A-T rich promoter on the DNA which is.
5 to 3 B. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. Hence RNA polymerase is considered as the one which decides the initiation of the transcription.
So an enzyme that attaches many pieces of DNA. These two strands serve as the template for the leading and lagging strands which will be created as DNA polymerase matches complementary nucleotides to the templates. 3 to 5 C.
Here we show that DNA polymerases from several hyperthermophilic archaea including Vent and Pfu specifically recognize the presence of uracil in a template strand and stall DNA synthesis before mutagenic misincorporation of adenine. As the replication progresses and the replisome moves forward DNA Polymerase III arrives at RNA primer and begins replicating DNA. Gene expression does not require any input of energy.
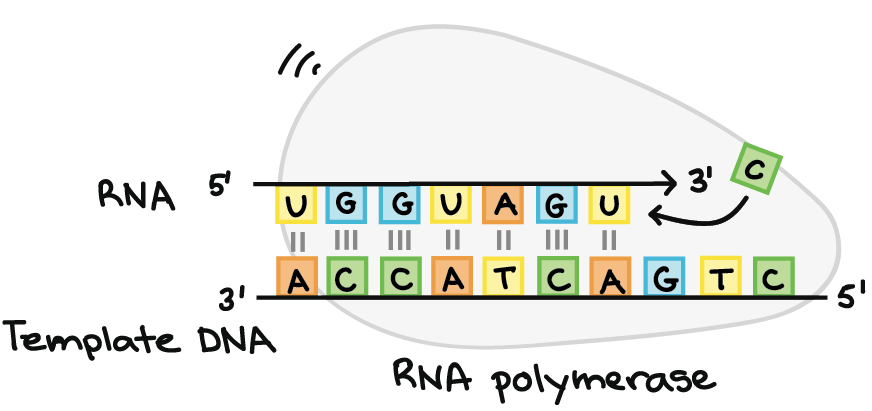
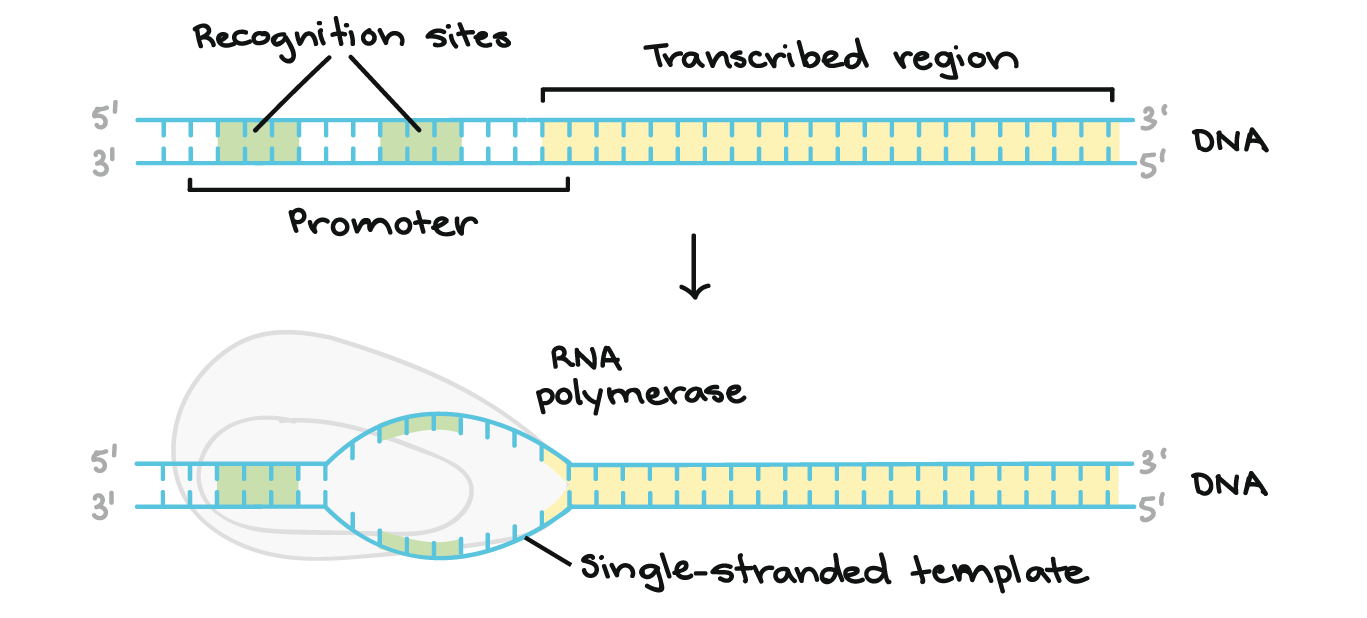
DNA Polymerase III is the primary enzyme involved in DNA replication. DNA polymerase reads the template strand in a _____ direction and adds nucleotides to the new strand in a _____ direction. Once transcription is initiated the DNA double helix unwinds and RNA polymerase reads the template strand adding nucleotides to the 3 end of the growing chain Figure 2b.
277 While Pol α initiates DNA synthesis Pol δ and Pol ε perform the majority of the DNA replication with Pol δ synthesizing the lagging strand and Pol ε synthesizing the leading strand. The template strand DNA is read by RNA polymerase in the 3-5 direction. A template strand is the term that refers to the strand used by DNA polymerase or RNA polymerase to attach complementary bases during DNA replication or RNA transcription respectively.
The process of DNA replication is catalyzed by a type of enzyme called DNA polymerase poly meaning many mer meaning pieces and ase meaning enzyme. The DNA template is used by RNA polymerase to produce a strand of RNA with a nucleotide sequence that is the same as the coding strand for the production of functional RNA units and mRNA for. In order for DNA polymerase to do this it must read the template strand from 3-5.
Basics of DNA Replication. DNA replication can proceed in either direction. Yes DNA polymerase uses a single-stranded DNA template in order to replicate DNA.
A sequence of DNA nucleotides that. An enzyme RNA polymerase reads the template strand to synthesis the RNA transcript by recognising the specific sequences. DNA replication is the cellular process involved in the synthesis of an exact copy of an existing DNA molecule.
It is often useful to distinguish the two strands of DNA -- the strand that is copied into mRNA and subsequently translated has the complementary sequence to the mRNA while the base sequence of the opposite strand directly corresponds to the codons in the mRNA. Each newly replicated molecule of DNA contains one conserved strand from the original DNA molecule. The leading strand is a new strand of DNA that is synthesized in a single continuous chain that.
DNA polymerase reads the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. DNA Polymerase synthesizes base pairs after strand separation at the origin of replication. Therefore replicating the template strand that runs 3-5 results in the synthesis of the leading strand.
DNA polymerases which are multisubunit enzymes including Pol α Pol δ and Pol ε are critical for the accurate replication of cellular DNA. The double helix of the original DNA molecule separates blue and new strands are made to match the separated. In the case of DNA polymerase.
During the replication process the double-helix of the DNA strand. It adds nucleotides to the 3end of the growing strand one nucleotide at a time. The terms template strand sense strand and coding strand are commonly used to describe one of the.
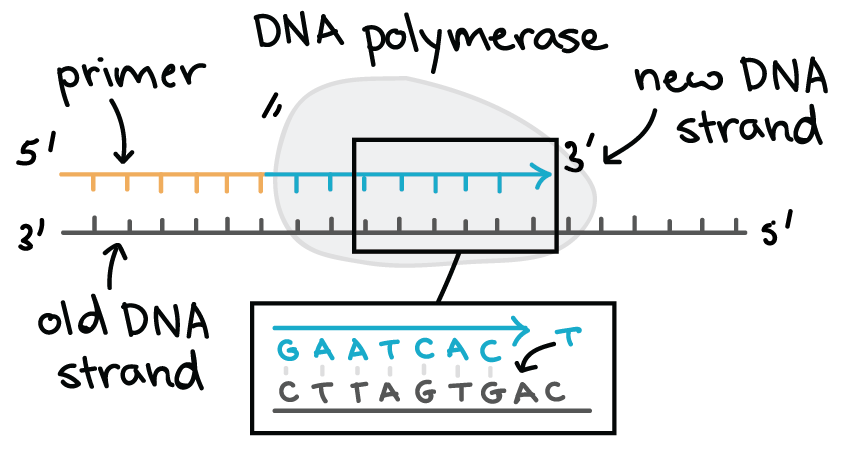
DNA Polymerase reads the template strand in _____ direction and builds the complementary daughter strand in _____direction. The DNA polymerase is the enzyme that joins individual nucleotides to produce a new strand of DNA it produces the sugar phosphate bonds that join the nucleotides together and it proof reads each new DNA strand so that each copy is a near perfect copy of the original. The RNA polymerase reads the non-coding or template strand from the 3-5 direction and polymerizes the RNA transcript by adding complementary nucleotides relative to the template strand.
Given the importance of accurate DNA replication the proper. DNA polymerase can only synthesize new strands of DNA in the 5-3 direction. The templates may be properly referred to as the leading strand template and the lagging strand template.
DNA is read by DNA polymerase in the 3 to 5 direction meaning. During DNA replication DNA polymerase reads the existingtemplate DNA strand while synthesizing a new complementary DNA strand to the template.
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
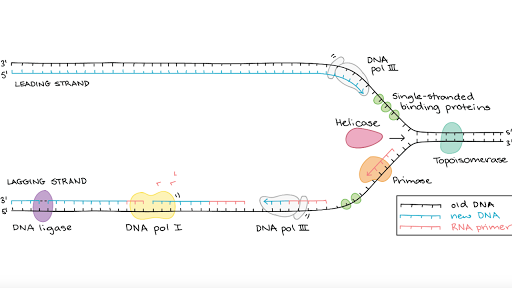
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Solved Which Of The Following Is True Regarding Dna Replication Ligase Synthesizes Most Of The Dna And Then Joins The Okazaki Fragments Together Dna Polymerase Iil Reads The Template Strand And Makes New

Rna Transcription Microbiology
Why Is The Template Strand From 3 To 5 In Transcription Quora

Dna Replication The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
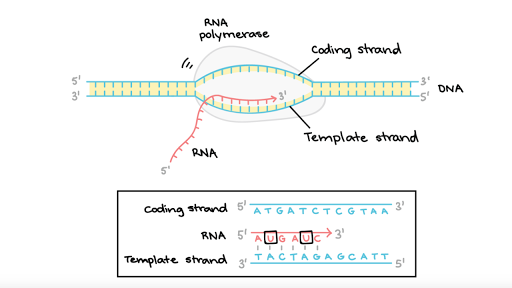
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
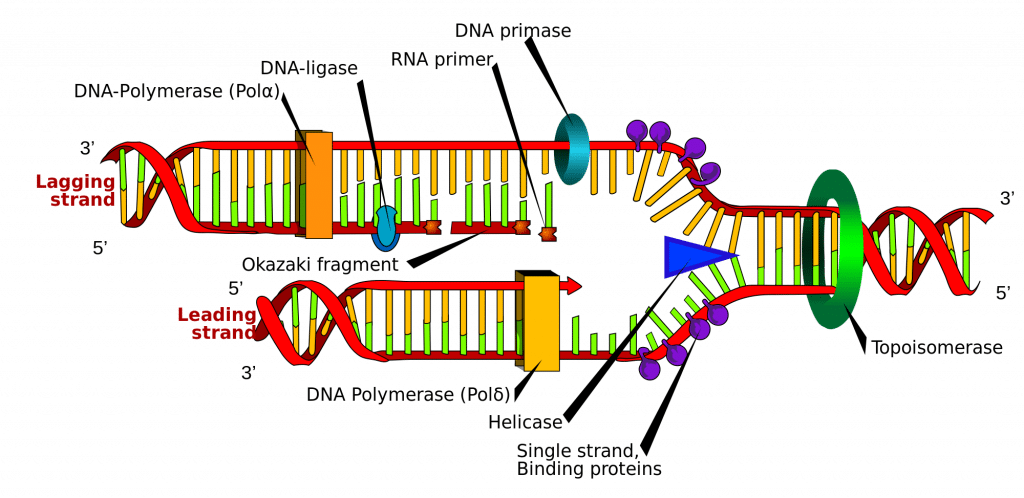
Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology
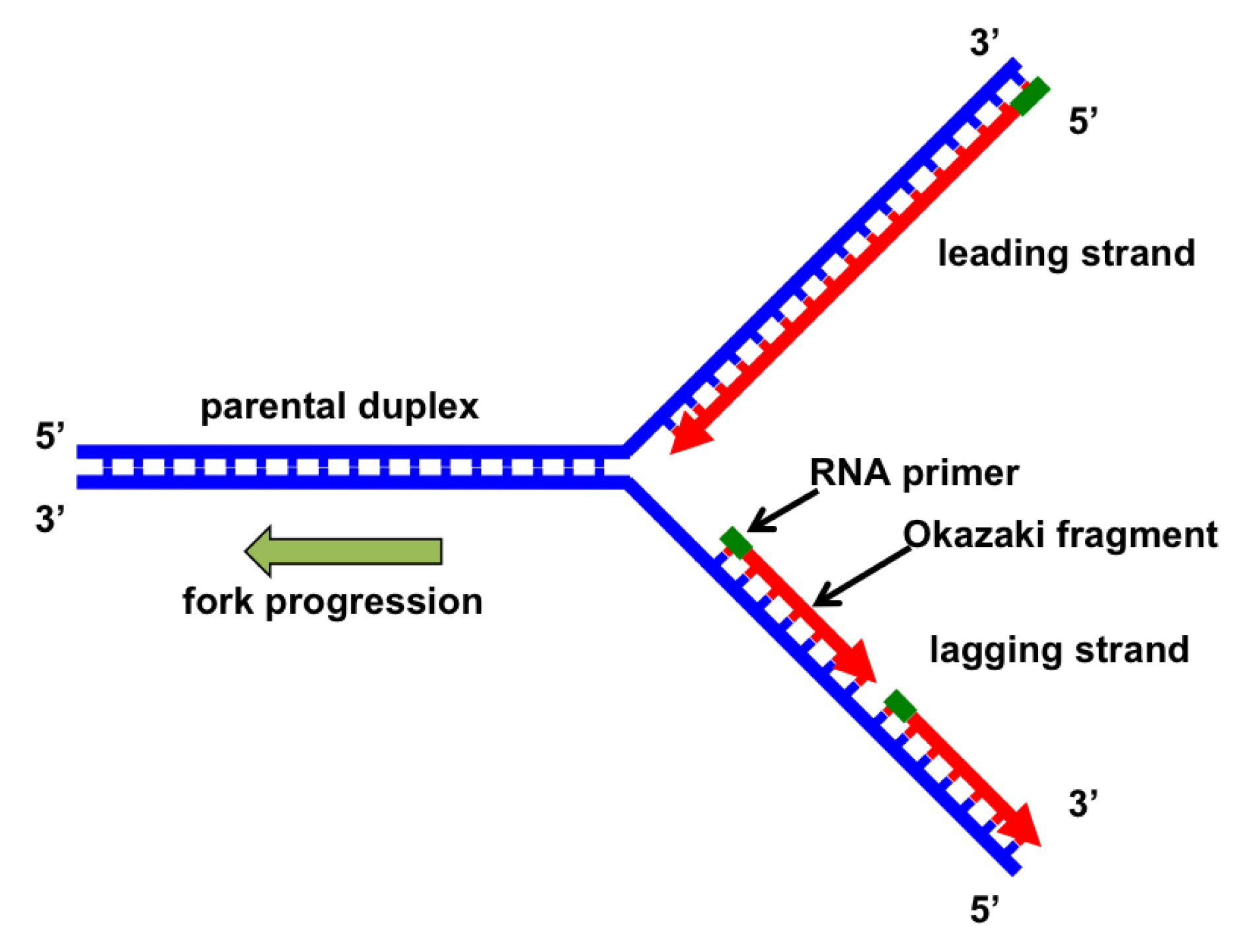
Genes Free Full Text The Replication Fork Understanding The Eukaryotic Replication Machinery And The Challenges To Genome Duplication Html
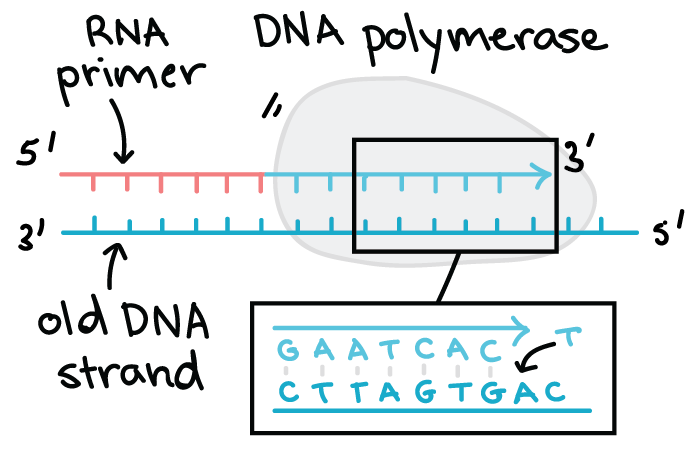
Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy

Dna Replication S Phase Checkpoint Control Learn Science At Scitable

Reading Basics Of Dna Replication Biology I

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable

Compatibility And Fidelity Of Mirror Image Thymidine In Transcription Events By T7 Rna Polymerase Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
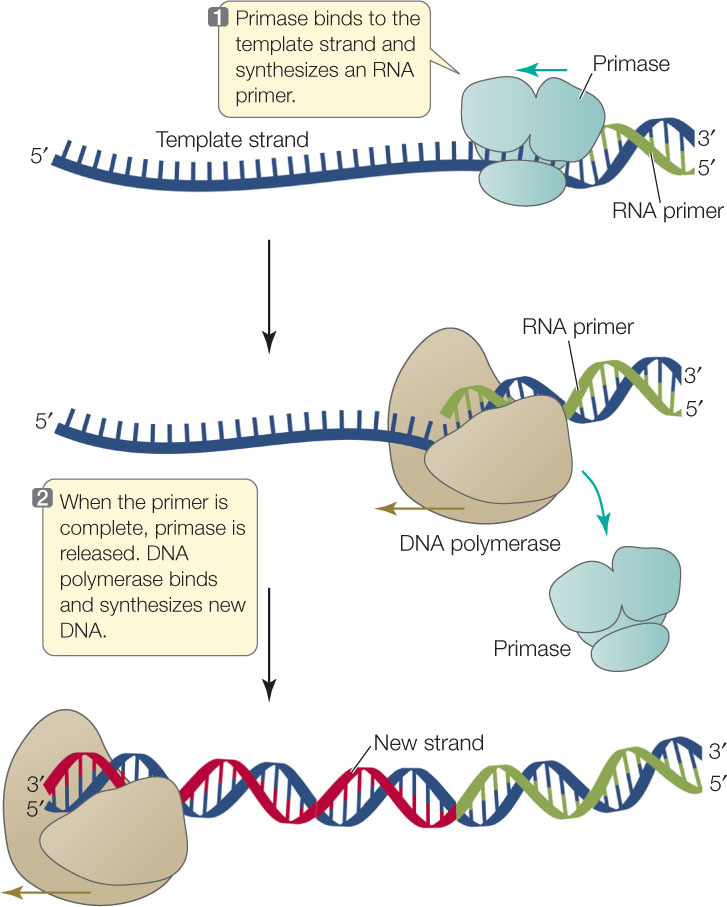
Comments
Post a Comment